Root Cavities
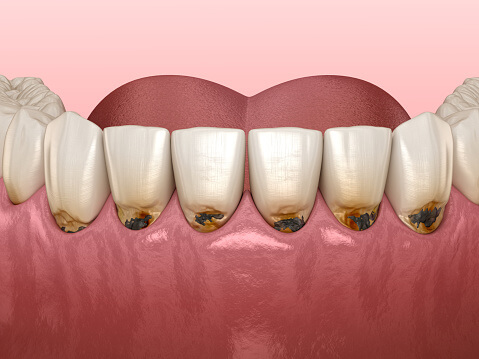
What Are Root Cavities?
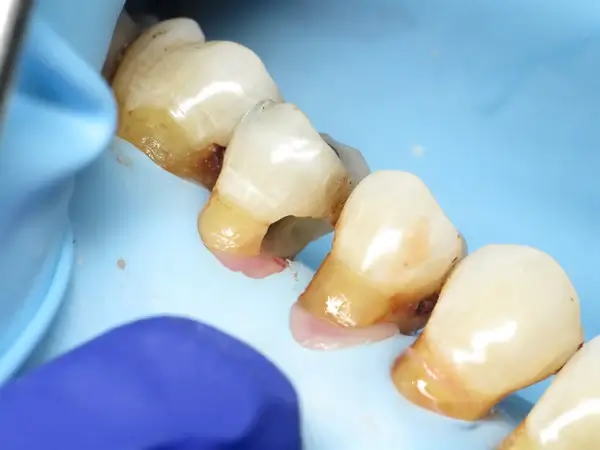
Root cavities are a specific type of dental decay that form on the root surface of a tooth, typically below the gumline. Unlike cavities on the crown of a tooth, root cavities occur when gum recession exposes the tooth’s roots. These areas lack the protective enamel layer found on the crown, making them more susceptible to decay.
Root cavities are most common in older adults with receding gums or gum disease, but anyone with exposed roots is at risk. If left untreated, root cavities can cause significant damage, leading to tooth loss.
Before you contact a Toronto dentist to examine Root Cavities, there are some things you should know as a patient:
- What Causes Root Cavities?
- Signs And Symptoms Of Root Cavities
- Treatment Options For Root Cavities
- Managing A Root Cavity Until You Can See The Dentist
- Cavity Risk Self Quiz
- Frequently Asked Questions About Root Cavities
If you have questions about Root Cavities or other dental problems, please contact us for more information.
What Causes Root Cavities?
Understanding the causes of root cavities can help you take proactive steps to prevent them. Here are the most common reasons root cavities develop:
- Gum Recession: Receding gums expose the tooth’s root, which lacks the protective enamel and is more prone to decay.
- Poor Oral Hygiene: Inadequate brushing and flossing allow plaque buildup, producing acids that erode the root surface.
- Dry Mouth: A lack of saliva reduces the natural cleansing of the mouth, increasing the risk of decay.
- High-Sugar Diet: Sugary foods and drinks feed bacteria, leading to acid production that damages the root surface.
- Tobacco Use: Smoking or using other tobacco products contributes to gum disease and gum recession, exposing tooth roots.
- Aging: As gums naturally recede with age, the exposed roots become more vulnerable to decay.
- Chronic Health Conditions: Conditions like diabetes can increase the risk of gum disease and dry mouth, which contribute to root cavities.
By taking steps to maintain good oral hygiene and avoiding sugary and acidic foods and drinks, you can significantly reduce your risk of developing cavities. If you have further questions about root cavities, please contact us.
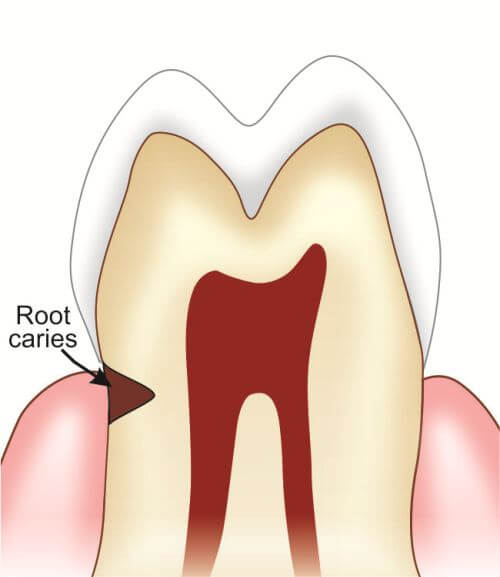
Signs and Symptoms of Root Cavities
Identifying root cavities early is crucial for effective treatment. Look for these common signs and symptoms:
- Tooth Sensitivity: Sharp or lingering sensitivity to hot, cold, or sweet foods and drinks.
- Visible Root Exposure: Exposed roots below the gumline often indicate gum recession, increasing the risk of decay.
- Persistent Toothache: Pain while chewing or constant discomfort may signal decay affecting the tooth’s nerve or structure.
- Gum Irritation: Red, swollen, or irritated gums near the affected tooth may indicate a root cavity.
- Discoloration Near the Gumline: Dark spots or discoloration on the tooth near the gumline suggest decay.
- Bad Breath: Chronic bad breath or an unpleasant taste in your mouth could result from bacteria in root cavities.
If you notice any of these symptoms, schedule a visit to your dentist promptly for an evaluation. If you have further questions about signs and symptoms of root cavities, please contact us.
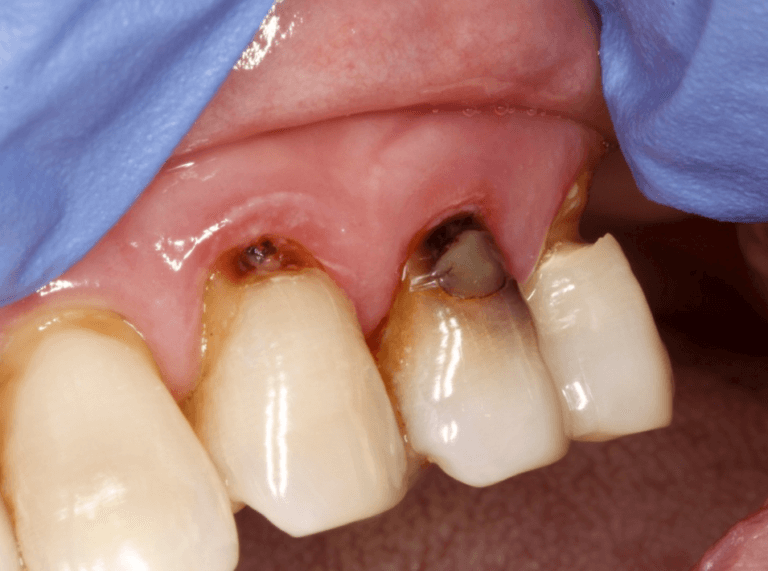
Treatment Options for Root Cavities
The appropriate treatment for root cavities depends on the severity of the decay. Common options include:
- Silver Diamine Fluoride (SDF): A non-invasive option to halt decay progression, particularly in patients who can’t undergo more extensive treatments.
- Fluoride Treatments: Early-stage cavities can sometimes be reversed with fluoride applications to remineralize the root surface.
- Dental Fillings: Decay is removed, and the cavity is filled with a tooth-colored material to restore function.
- Root Canal Therapy: Severe decay affecting the tooth’s pulp may require a root canal to remove infected tissue.
- Dental Crowns: For extensive decay, a crown can restore the tooth’s structure and protect it from further damage.
- Gum Grafting: Receding gums exposing the roots may be treated with gum grafting to protect against future decay.
Prompt treatment is essential to prevent further complications and avoid tooth loss. If you have further questions about root cavity treatment options, please contact us.
Managing A Root Cavity Until You Can See The Dentist
If you suspect you have a root cavity but can’t get to the dentist right away, you can take the following steps to manage the symptoms:
- Rinse with saltwater to reduce pain and inflammation.
- Use over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen for discomfort.
- Avoid hard, sticky, or sugary foods that can worsen the root cavity.
- Apply temporary fillings (available at drugstores) to protect the root cavity until your dental appointment.
- Practice good oral hygiene to prevent the root decay from getting worse.
These measures are only temporary. It’s important to visit your dentist as soon as possible to address the cavity and avoid further damage. If you have further questions about managing Cavities, please contact us.
Cavity Risk Self Quiz
Try Our free online dental caries risk assessment quiz based on the California Dental Association’s Caries Management by Risk Assessment (CAMBRA) designed for patients aged 6 years and older. This caries risk assessment tool is meant to give you an idea of your level of dental caries risk, and by no means substitute for an oral exam by a dental professional. Please contact us for a more complete examination.
Frequently Asked Questions About Root Cavities
- Can root cavities be reversed?
Root cavities in their early stages may be remineralized with fluoride treatments, but advanced decay requires intervention like fillings or root canals.
- Are root cavities more common in older adults?
Yes, older adults are at higher risk due to gum recession, which exposes the roots of teeth, making them vulnerable to decay.
- How can I tell if I have a root cavity?
Look for symptoms like sensitivity, pain near the gumline, discoloration, or exposed roots. A dental check-up is essential for confirmation.
- What toothpaste is best for preventing root cavities?
A high-fluoride toothpaste like Colgate PreviDent 5000 is ideal for protecting exposed roots and strengthening enamel.
If you’re experiencing symptoms of root cavities or want to learn more about prevention, contact us at Atlas Dental. Our expert team is here to provide personalized care and ensure your oral health is in top condition.