Bleeding Gums
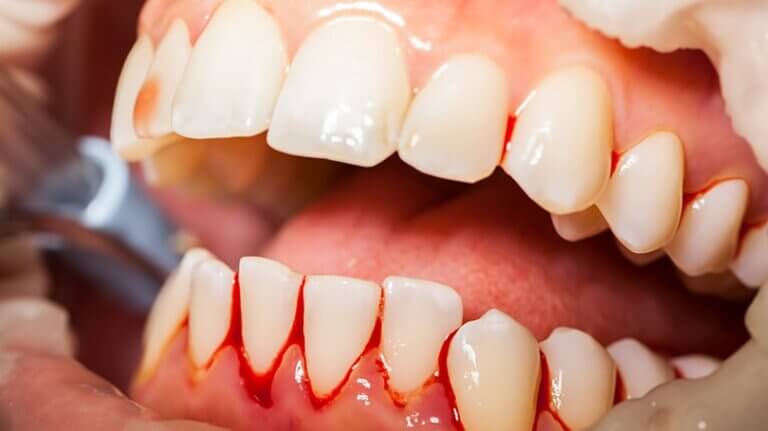
What Are Bleeding Gums?
Bleeding gums are a common yet serious oral health issue that should never be ignored. Whether you notice blood while brushing your teeth or after biting into an apple, bleeding gums can signal a range of dental concerns. Known as gingival bleeding, this condition occurs when the gums bleed easily—either spontaneously or with mild pressure, like brushing. Addressing bleeding gums promptly is essential to maintaining healthy gums and teeth.
Before you contact a Toronto dentist to examine Bleeding Gums, there are some things you should know as a patient:
- Why Do I Have Bleeding Gums?
- Signs And Symptoms Of Bleeding Gums
- Treatment Options For Bleeding Gums
- How To Prevent Bleeding Gums
- Managing Bleeding Gums Until You Can See The Dentist
- Frequently Asked Questions About Bleeding Gums
If you have questions about Bleeding Gums or other dental problems, please contact us for more information.
Why Do I Have Bleeding Gums?
Several factors can contribute to bleeding gums. Here are the most common causes:
- Poor Oral Hygiene: Inadequate brushing and flossing can cause plaque to accumulate along the gumline, leading to inflammation (gingivitis) and bleeding gums.
- Gingivitis: The earliest stage of gum disease, gingivitis, causes red, swollen gums that bleed easily due to bacterial buildup.
- Plaque and Tartar Buildup: When plaque hardens into tartar, it irritates the gums, leading to inflammation and bleeding.
- Hormonal Changes: Hormonal shifts during pregnancy or puberty can make gums more sensitive and prone to bleeding.
- Medications: Some medications, such as blood thinners, can cause bleeding gums as a side effect.
- Nutritional Deficiencies: A lack of vitamin C or vitamin K can weaken gums, increasing the risk of bleeding.
- Smoking: Tobacco use impairs gum health, reducing blood flow and slowing healing, which leads to bleeding gums.
- Systemic Diseases: Conditions like diabetes and leukemia can affect your gums, making them more prone to bleeding.
Knowing the cause of your bleeding gums is the first step toward treatment. Schedule regular dental check-ups and maintain good oral hygiene to keep your gums healthy. For more information about Bleeding Gums, please contact us.
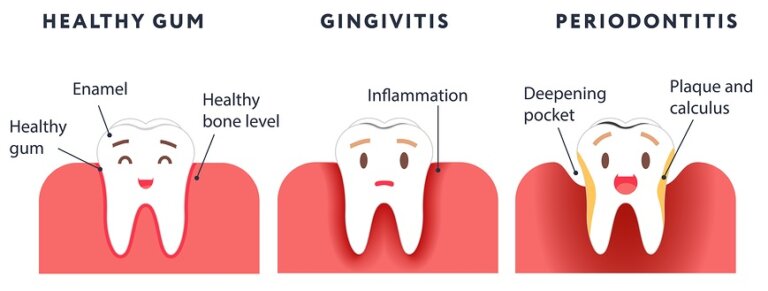
Signs And Symptoms Of Bleeding Gums
Recognizing the signs of bleeding gums can help prevent more severe gum disease. Common symptoms include:
- Easy Bleeding: Gums that bleed when brushing, flossing, or spontaneously are a major warning sign.
- Red, Swollen Gums: Inflammation causes gums to become puffy, red, and more likely to bleed.
- Bad Breath (Halitosis): Poor oral hygiene allows bacteria to thrive, leading to gum inflammation and bleeding, along with persistent bad breath.
- Receding Gums: Gums pulling away from the teeth can be a sign of periodontitis (advanced gum disease), often accompanied by bleeding.
- Sensitive Gums: Tenderness around bleeding areas indicates inflammation.
- Pain or Discomfort: Gum inflammation can cause discomfort or pain, particularly when eating or brushing.
- Pus Between Gums and Teeth: This is a sign of advanced gum disease and often accompanies bleeding.
- Loose Teeth: In severe cases, the gums’ support structures weaken, leading to loose teeth.
Early detection of these symptoms allows for timely treatment, preventing further damage. For more information about Bleeding Gums, please contact us.
Treatment Options For Bleeding Gums
Treating bleeding gums involves both professional dental care and good oral hygiene practices at home:
- Professional Cleaning: Dental hygienists remove plaque and tartar, addressing gum inflammation and bleeding.
- Scaling and Root Planing: For advanced cases of gum disease, deep cleaning below the gumline can reduce bleeding and promote gum reattachment.
- Gum Surgery: In severe cases, gum surgery may be needed to repair damaged tissues.
- Regular Dental Visits: Frequent check-ups help monitor gum health and prevent minor issues from worsening.
By combining professional treatments with consistent oral hygiene, you can manage and prevent bleeding gums. For more information about Bleeding Gums, please contact us.
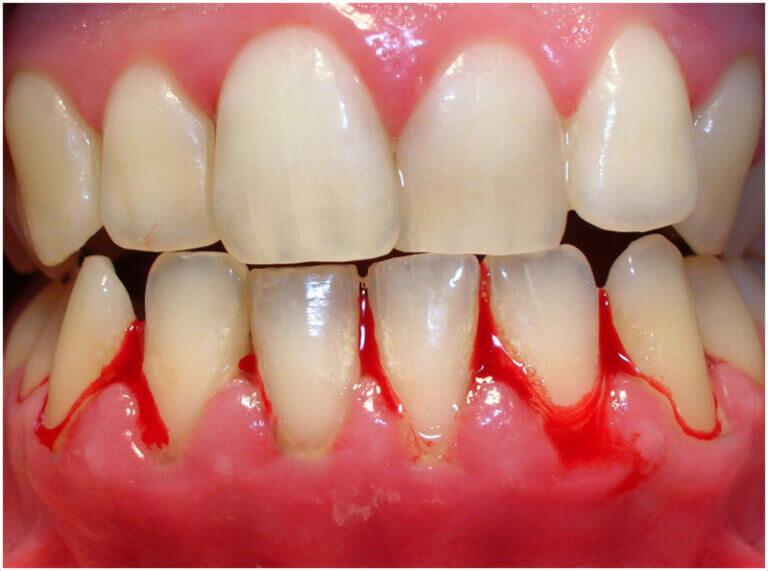
How To Prevent Bleeding Gums
Preventing bleeding gums is easier with the right oral care habits. Follow these steps to maintain healthy gums:
- Brush and Floss Daily: Use fluoride toothpaste and floss to remove plaque and prevent gum inflammation. Consider using an alcohol-free mouthwash to reduce bacteria without irritating the gums.
- Use a Soft-Bristled Toothbrush: Soft bristles are gentler on the gums while still effectively cleaning your teeth.
- Visit Your Dentist Regularly: Schedule routine cleanings and exams to detect early signs of gum disease.
- Eat a Balanced Diet: Nutrients like vitamin C and vitamin K are vital for healthy gums. A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains supports overall oral health.
- Limit Sugary Foods: Reduce sugary and acidic food intake, as they can promote plaque buildup and gum inflammation.
- Quit Smoking: Smoking impairs gum health and slows healing, increasing the risk of gum disease.
Commit to these habits, and you’ll significantly lower your chances of experiencing bleeding gums. For more information about Bleeding Gums, please contact us.
Managing Bleeding Gums Until You Can See The Dentist
If you notice bleeding gums and can’t visit the dentist right away, try these at-home remedies:
- Gentle Brushing and Flossing: Continue brushing and flossing, but use a soft-bristled toothbrush and avoid aggravating your gums.
- Saltwater Rinse: Rinse with warm salt water to reduce bacteria and soothe inflammation.
- Apply Pressure: If gums are bleeding, gently press with clean gauze to control bleeding.
- Avoid Irritants: Stay away from spicy, hot, or acidic foods, and avoid smoking.
- Pain Relief: Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen, can help alleviate discomfort.
- Cold Compress: Apply a cold compress to reduce swelling and soothe irritated gums.
These remedies can help manage symptoms, but make sure to see your dentist for a full evaluation and treatment. For more information about Bleeding Gums, please contact us.
Frequently Asked Questions About Bleeding Gums
- Is it normal for gums to bleed when brushing or flossing?
Occasional bleeding may happen if you’re brushing too hard or starting a new flossing routine. However, persistent bleeding can indicate gum disease and should be checked by a dentist.
- Can bleeding gums heal on their own?
Mild cases may improve with proper oral hygiene, like regular brushing and flossing. If the bleeding persists, professional treatment may be necessary to address underlying issues.
- Does stress cause bleeding gums?
Yes, stress can weaken your immune system, making it harder for your gums to fight off infections like gingivitis. Managing stress and maintaining good oral care can help reduce this risk.
- Are bleeding gums a sign of a serious health issue?
Bleeding gums can be a symptom of gum disease, but they may also indicate other health problems, such as vitamin deficiencies or diabetes. It’s important to consult your dentist for a proper evaluation.
Bleeding gums are often a sign that your oral health needs attention, but they can usually be treated with proper care and professional guidance. For more information about Bleeding Gums, please contact us.