Dental Bone Loss
What Is Dental Bone Loss?
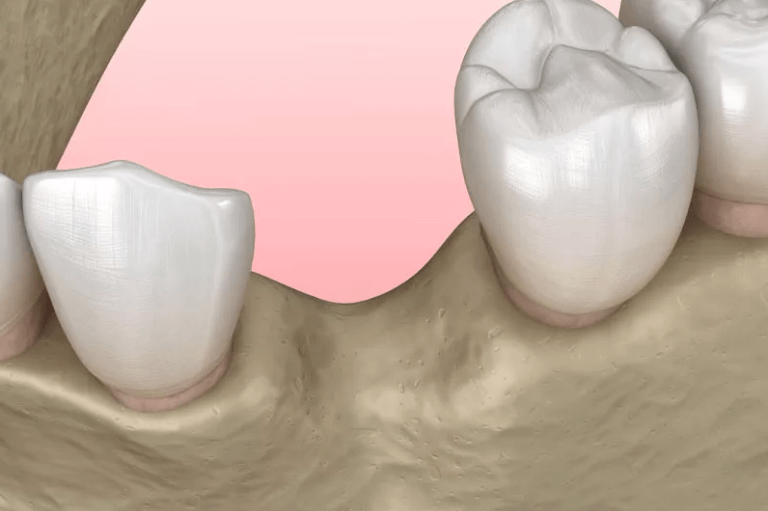
Dental bone loss, also known as periodontal or alveolar bone resorption, occurs when the bone tissue supporting the teeth diminishes. This condition often results from gum disease, poor oral hygiene, or missing teeth, leading to potential complications like further loose teeth, receding gums, and further bone resorption. Moreover, insufficient bone volume may hinder the success of dental implant procedures.
Before visiting your Toronto dentist for an examination of dental bone loss, here are some important points to consider:
- Why Do I Have Dental Bone Loss?
- Signs And Symptoms Of Dental Bone Loss
- Treatment Options For Dental Bone Loss
- Managing Dental Bone Loss Until You Can See The Dentist
- Frequently Asked Questions About Dental Bone Loss
If you have questions about Dental Bone Loss or other dental problems, please contact us for more information.
Why Do I Have Dental Bone Loss?
Several factors can contribute to dental bone loss. Common causes include:
- Poor Oral Hygiene: Inadequate brushing and flossing allow plaque and bacteria to build up, increasing the risk of gum disease and bone loss.
- Gum Disease: Conditions like gingivitis and periodontitis can lead to bone deterioration as bacteria cause inflammation in the gums, which can spread to the supporting bone.
- Tooth Loss: Missing teeth can result in the surrounding bone tissue shrinking, which may lead to further tooth and bone loss over time.
- Cracked Tooth Syndrome or Vertical Root Fracture: Cracks in teeth can cause localized bone loss. In such cases, the affected tooth is often unsalvageable and must be extracted.
- Smoking: Tobacco use weakens the immune system and damages gum tissue, making it easier for bacteria to cause infections that lead to bone loss.
- Genetics: Some individuals are genetically predisposed to gum disease and bone loss due to inherited factors.
- Medical Conditions: Osteoporosis and certain medications can increase the risk of dental bone loss.
By understanding the factors that can contribute to dental bone loss, you can take steps to prevent this condition and protect your dental health. For more information about Dental Bone Loss, please contact us.
Signs and Symptoms of Dental Bone Loss
Dental bone loss can develop gradually, so it’s essential to watch for early warning signs. If you experience any of the following, it’s time to consult a dentist:
- Receding Gums: Gums pulling away from the teeth can make them appear longer.
- Loose Teeth: Bone loss can cause teeth to feel loose or even fall out.
- Bite Changes: A shift in the way your teeth align when biting or chewing may indicate bone loss.
- Tooth Sensitivity: Exposed roots due to gum recession can cause increased sensitivity to hot or cold foods.
- Pain or Discomfort: Bone loss may result in pain around the affected area.
- Bad Breath: Chronic bad breath or a persistent bad taste can be a sign of periodontal disease they can contribute to bone loss.
Early intervention can prevent further damage. For more information about the signs and symptoms of Dental Bone Loss, please contact us.
Treatment Options for Dental Bone Loss
Treatment for dental bone loss depends on its severity and underlying cause. Common treatment options include:
- Deep Cleaning (Scaling and Root Planing): This procedure removes plaque and bacteria from below the gum line, promoting healing and preventing further bone loss.
- Bone Grafting: Severe cases may require a bone graft to rebuild the lost bone and support dental implants or natural teeth.
- Periodontal Surgery: Reducing pocket depth and repairing gum health can help halt bone loss progression.
- Tooth Extraction: Severely damaged teeth may need to be extracted. Replacement options include dental implants or bridges.
- Dental Implants: Implants are artificial tooth roots surgically placed into the jawbone to support replacement teeth. Adequate bone volume is essential, and bone grafting may be required if the bone is insufficient.
- Dental Bridges: Bridges use surrounding teeth to support a replacement tooth, offering an alternative to implants.
- Dentures: Removable dentures can replace missing teeth, and they may be more appropriate for individuals with severe bone loss who are not candidates for implants.
If you are concerned about dental bone loss and want to learn more about your treatment options, do not hesitate to contact us. With proper treatment and care, you can protect your dental health and enjoy a healthy, beautiful smile for years to come.
Managing Dental Bone Loss Until You Can See the Dentist
If you’re dealing with dental bone loss but can’t see a dentist immediately, here are some steps to manage your symptoms:
- Practice Excellent Oral Hygiene: Gently brush and floss around the affected area. Use salt water rinses or over-the-counter mouthwash to reduce inflammation and bacteria.
- Over-the-Counter Pain Relief: Use pain relievers like ibuprofen (Advil) or acetaminophen (Tylenol) as needed to manage discomfort.
- Cold Compresses: Applying cold compresses to your face can help reduce swelling and pain.
- Avoid Hard or Chewy Foods: Stick to softer foods to minimize pressure on your teeth and gums.
- Avoid Smoking: Smoking can worsen bone loss, so it’s best to refrain until you can receive professional care.
These tips are temporary solutions until you can see your dentist. Dental bone loss will progress without proper treatment, so be sure to contact us for more information.
Frequently Asked Questions About Dental Bone Loss
- Can dental bone loss be reversed?
While bone loss is often irreversible, treatments like bone grafting or guided tissue regeneration can help restore lost bone to some extent. Early intervention and maintaining good oral hygiene are crucial to prevent further deterioration.
- How is dental bone loss diagnosed?
Dentists diagnose bone loss through clinical examinations and imaging techniques such as periapical and bitewing X-rays, which provide detailed views of the teeth and supporting bone structures.
- How does smoking affect dental bone health?
Smoking impairs blood flow to the gums, weakening the immune system and making it easier for infections to develop, which can accelerate bone loss.
- What are the risks of untreated dental bone loss?
Untreated bone loss can lead to loose teeth, tooth loss, changes in facial structure, and difficulties with chewing and speaking. It may also complicate future dental treatments, such as the placement of dental implants.
Addressing dental bone loss promptly is essential for preserving oral health and preventing complications like tooth loss and facial structure changes. Contact us at Atlas Dental to explore prevention and treatment options tailored to your needs.