Dental Sinus Infection

What Is A Dental Sinus Infection?
A Sinus Infection, also called sinusitis, occurs when the sinuses—air-filled cavities in the skull located near the forehead, cheeks, and eyes—become inflamed or infected. This inflammation can lead to symptoms like facial pain, pressure, congestion, and headaches due to mucus buildup. While often associated with respiratory issues, sinus infections can sometimes stem from dental problems. This is particularly true for dental infections related to the maxillary sinuses, which are located above the upper molars and premolars.
When bacteria spread from the teeth or gums into the maxillary sinuses, it can cause a dental sinus infection, often resulting in referred pain in the teeth and jaw. Understanding the connection between dental health and sinus issues is crucial for effective treatment. Before you contact a Toronto dentist to examine a potential Sinus Infection of dental origin, there are some things you should know as a patient:
- Common Causes of Dental-Origin Sinusitis
- Signs and Symptoms of A Dental Sinus Infection
- How To Diagnose Dental Sinus Infection
- Treatment Options for Dental Sinus Infection
- Managing Dental Sinus Infection Until You Can See The Dentist
- Frequently Asked Questions About Dental Sinus Infection
If you have questions about Sinus Infection or other dental problems, please contact us for more information.
Causes of Dental-Origin Sinusitis
Several factors can contribute to dental-related sinus infections:
- Dental Infections: Bacteria from gum disease or tooth infections can spread into the sinuses, causing inflammation.
- Barotrauma: Changes in air pressure from dental procedures or air travel can lead to sinus inflammation.
- Allergies: Reactions to pollen, dust, or pet dander can irritate the sinuses.
- Dental Procedures: Certain procedures, like tooth extractions or implants, can create sinus perforations, increasing infection risk.
- Smoking: Smoking weakens the immune system and irritates sinus linings, making infection more likely.
- Nasal Polyps: Small growths in the sinuses or nasal passages can block airflow, increasing the risk of infection.
- Weak Immune System: A weakened immune system from illness or medication can make sinus infections more likely.
Each of these factors can interact to increase sinus infection risk. If you’re experiencing sinus pain and suspect it may be dental-related, contact us to discuss your symptoms.
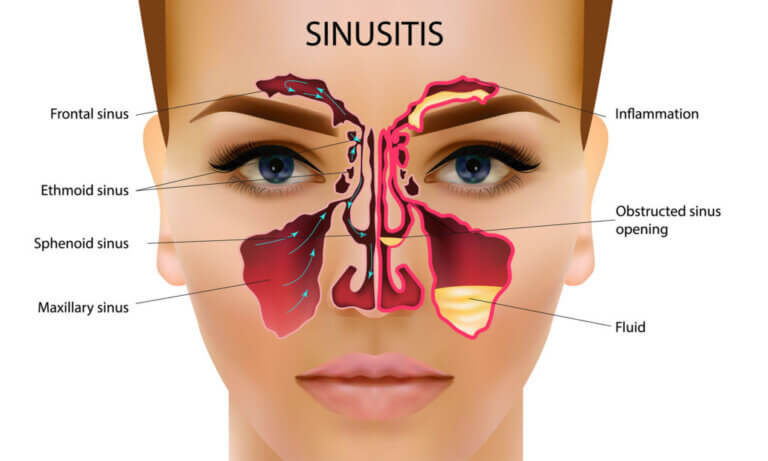
Signs and Symptoms of A Dental Sinus Infection
If you suspect a dental sinus infection, watch for these signs:
- Pain and Pressure: Aching around the cheeks and forehead, often accompanied by a headache.
- Tooth Pain: Especially in the upper back teeth, which are close to the maxillary sinuses.
- Nasal Congestion: Mucus buildup and potential drainage.
- Tenderness and Swelling: Pain around the sinuses, sensitive to touch.
- Bad Breath: Caused by trapped mucus and bacteria in the sinuses.
- Fatigue and Fever: Bacterial infections can lead to general fatigue and fever.
- Ear Pain: Referred pain from sinus pressure may be felt in the ears.
If you experience these symptoms, an early evaluation by your dentist is essential to prevent more severe complications. If you have further questions about signs and symptoms of Dental Sinus Infection, please contact us.
How To Diagnose Dental Sinus Infection
f you think you might have a dental sinus infection, your dentist can perform these diagnostic steps:
- Intra-Oral Exam: A close look at the affected tooth and surrounding gums to spot infection signs.
- Dental X-rays: 2D X-rays, such as periapical or panoramic images, can reveal tooth decay or abscesses.
- CBCT Scan: A Cone Beam CT scan offers detailed 3D imaging of the teeth and sinuses, ideal for detecting infection or sinus inflammation.
Your dentist may also review your medical history and symptoms to accurately diagnose the infection and recommend a personalized treatment plan. If you have further questions about how to diagnose a Dental Sinus Infection, please contact us.
Treatment Options for Dental Sinus Infection
Treatment varies depending on the infection’s cause and severity:
- Antibiotics: Prescribed to treat bacterial infections.
- Tooth Extraction: If the infection originates from a decayed or infected tooth, removal may be necessary.
- Root Canal Therapy: This procedure removes infected tissue from inside the tooth, helping save it and prevent further infection.
- Sinus Surgery: In severe cases, surgery may be needed to drain the sinuses or remove infected tissue. This procedure is often performed by an ENT specialist.
Follow your dentist’s instructions carefully and complete the full course of treatment to ensure a full recovery. If you have further questions about treatment options for a Sinus Infection of dental origin, please contact us.
Managing Dental Sinus Infection Until You Can See The Dentist
While waiting for a dental appointment, you can manage symptoms in the following ways:
- Pain Relief: Over-the-counter medications like acetaminophen or ibuprofen can relieve pain and reduce inflammation.
- Oral Hygiene: Maintain oral hygiene by brushing gently and rinsing with salt water to reduce infection and pain.
- Warm Compresses: Apply a warm compress to reduce pain and sinus pressure.
- Nasal Decongestants: Over-the-counter decongestants can relieve congestion.
- Steam Inhalation: Inhaling steam from a hot shower or bowl of water can help open sinuses.
- Humidifier: Adding moisture to the air can soothe sinus passages.
- Saline Nasal Irrigation: Flush the nasal passages with a saline solution to reduce mucus and inflammation.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking water helps thin mucus for easier drainage.
These methods can offer temporary relief but are not substitutes for professional treatment. If you have further questions about how to manage a dental Sinus Infection, please contact us.
Frequently Asked Questions About Dental Sinus Infection
- Can a dental sinus infection resolve on its own?
While some sinus infections may improve without treatment, dental-origin sinus infections often require professional intervention to address the underlying dental issue.
- Is a dental sinus infection a medical emergency?
While not always an emergency, a dental sinus infection requires prompt attention to prevent the infection from spreading further or causing more severe health problems.
- Can allergies exacerbate a dental sinus infection?
Yes, allergies causing sinus inflammation can worsen the symptoms of a dental sinus infection, as the sinuses may already be congested or inflamed.
- Is surgery ever required for dental sinus infections?
In rare cases where the infection doesn’t respond to antibiotics or becomes chronic, surgical intervention like sinus drainage or addressing the infected tooth may be necessary.
Dental sinus infections require prompt diagnosis and treatment to address both the dental and sinus-related issues effectively. If you have further questions about how to manage a dental Sinus Infection, please contact us.