External Root Resorption
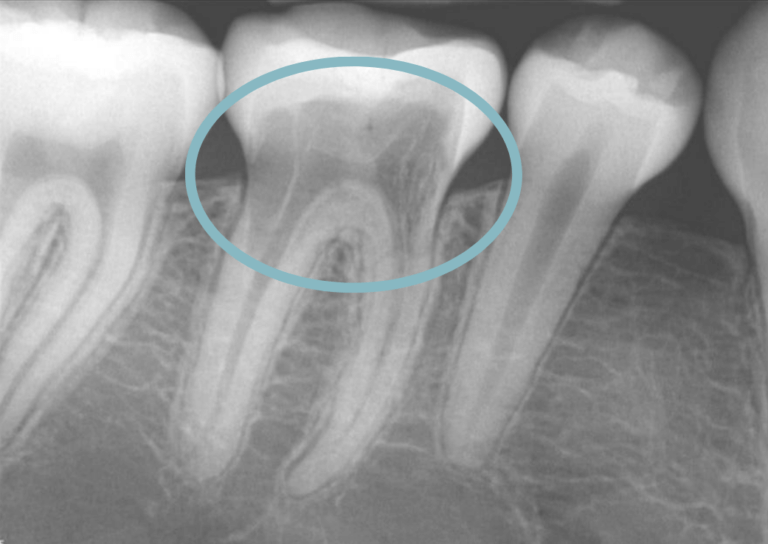
What Is External Root Resorption?
External root resorption is a dental condition where the body’s immune system mistakenly targets the external surface of a tooth’s root, causing it to break down. Unlike internal root resorption, which damages the tooth from the inside, external root resorption affects the outside-in, compromising the tooth’s stability and health. If untreated, this process can lead to tooth sensitivity, discomfort, and even tooth loss.
Before you contact a Toronto dentist to examine External Root Resorption, there are some things you should know as a patient:
- Key Causes of External Root Resorption
- Signs And Symptoms Of External Root Resorption
- Treatment Options For External Root Resorption
- Frequently Asked Questions About External Root Resorption
If you have questions about External Root Resorption or other dental problems, please contact us for more information.
Key Causes of External Root Resorption
External root resorption can develop for a variety of reasons. Some common causes include:
- Trauma to the Teeth: Physical trauma, such as injuries or accidents, can initiate the resorption process by damaging the root structure.
- Orthodontic Treatment: Pressure from braces or other orthodontic appliances can sometimes contribute to root resorption. Dental professionals typically monitor for this, but it can still occur.
- Inflammatory Conditions: Autoimmune disorders or systemic inflammatory conditions can increase the likelihood of resorption by altering the body’s immune response to the teeth.
- Chronic Dental Infections: Untreated infections, like dental abscesses, create an environment where root resorption may thrive due to inflammation and bacterial activity.
- Genetic Factors: Genetics may play a role, with some people inherently more predisposed to resorption than others.
- Age-Related Changes: As people age, their dental structures change, which may increase the risk of resorption.
- Idiopathic Causes: In certain cases, resorption may occur without a clear cause, highlighting the complexity of this condition.
Understanding these potential causes can help individuals work with their dentist to monitor risk factors and take preventive steps. For more information about External Root Resorption, please contact us.
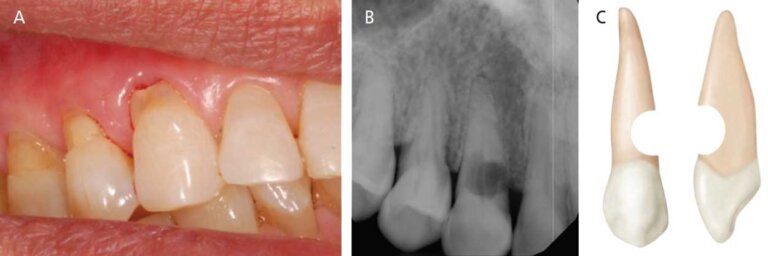
Signs And Symptoms Of External Root Resorption
Early identification of external root resorption is essential for effective treatment. Be aware of these key symptoms:
- Tooth Sensitivity: Increased sensitivity to hot, cold, or sweet foods and drinks may be a sign of root resorption, as the outer layers of the tooth wear away and expose nerves.
- Tooth Discoloration: Discoloration, often appearing as pink or dark spots, indicates breakdown within the tooth structure.
- Swelling and Discomfort: Gum swelling around a specific tooth, along with localized discomfort, may signal resorption.
- Tooth Mobility: A loose or mobile tooth without an apparent cause may be indicative of root resorption, as the root structure deteriorates.
- Pain During Chewing or Touch: Pain when chewing or touching the affected tooth may suggest that the root has been compromised.
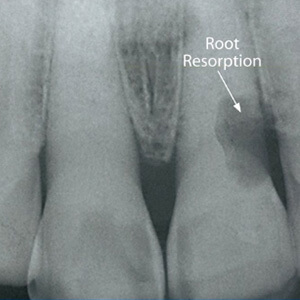
- Visible Changes on Dental X-rays: Dental X-rays are vital for detecting external root resorption, often revealing changes in root shape or density that aren’t visible to the naked eye.
If you experience any of these signs, schedule a dental examination to confirm the cause and receive prompt treatment. For more information about External Root Resorption, please contact us.
Treatment Options For External Root Resorption
Treatment for external root resorption varies based on the severity and location of the resorption:
- Root Canal Therapy: If the pulp inside the tooth is affected, root canal therapy may be necessary. This involves removing damaged tissue, then sealing and filling the tooth to protect against further damage.
- Surgical Intervention: For severe cases, surgery may be required to access the affected root area, remove damaged tissue, and repair the tooth’s structure.
- Tooth Extraction and Replacement: In instances where the damage is too extensive for other treatments, extraction may be recommended. Replacement options include dental implants or bridges to restore dental function and aesthetics.
- Preventive Strategies: Regular dental check-ups, along with imaging, are essential to detect early signs of root resorption. Patients with a history of orthodontic treatment, trauma, or inflammatory conditions may benefit from more frequent monitoring.
Individuals experiencing external root resorption should consult with their dentist to determine the most suitable course of action based on their specific situation. For more information about External Root Resorption, please contact us.
Frequently Asked Questions About External Root Resorption
- Can external root resorption be prevented?
While prevention isn’t always possible, regular dental visits and proper oral hygiene can reduce risks. Dental professionals can monitor high-risk individuals to catch early signs of resorption.
- How is external root resorption diagnosed?
External root resorption is typically identified through periapical X-rays, which can reveal changes in the root structure. Dentists may also observe symptoms like sensitivity, discoloration, or tooth mobility.
- Is external root resorption painful?
In early stages, resorption might not cause pain. However, as the resorption progresses, it can lead to sensitivity, discomfort, and pain, especially during chewing.
- Who is at the highest risk for external root resorption?
Individuals with a history of trauma, orthodontic treatment, chronic dental infections, or systemic inflammatory conditions may be at a higher risk. Aging and genetic predispositions also contribute.
External root resorption is a serious dental condition that requires prompt diagnosis and treatment to preserve tooth health and stability. For more information about External Root Resorption, please contact us.