Internal Root Resorption
What Is Internal Root Resorption?
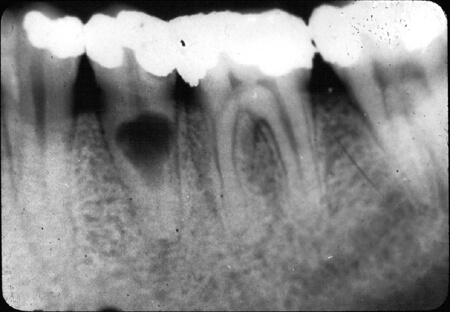
Internal root resorption is an uncommon dental condition where the inner structure of a tooth’s root begins to break down. Unlike external root resorption, which affects the outer surface, internal root resorption starts within the root canal and can compromise the tooth’s stability. While often painless in early stages, it can eventually cause discomfort and, if left untreated, may lead to tooth loss. Early detection and management by a dental professional are crucial for preserving the affected tooth.
Before you contact a Toronto dentist to examine Internal Root Resorption, there are some things you should know as a patient:
- What Causes Internal Root Resorption?
- Signs And Symptoms Of Internal Root Resorption
- Treatment Options For Internal Root Resorption
- Frequently Asked Questions About Internal Root Resorption
If you have questions about Internal Root Resorption or other dental problems, please contact us for more information.
What Causes Internal Root Resorption?
Understanding the factors contributing to internal root resorption can help in both preventing and managing the condition. Here are the most common causes:
- Trauma to the Tooth: A strong impact, such as from an accident or sports injury, can disrupt the internal cellular balance of a tooth, initiating resorption.
- Previous Dental Procedures: Certain dental treatments, especially root canal therapy, may sometimes lead to root resorption due to changes in the tooth’s internal environment.
- Chronic Infections: Long-standing infections like dental abscesses can create conditions that encourage internal resorption by weakening the tooth structure.
- Genetic Predisposition: Some individuals have a genetic inclination toward dental conditions, including internal resorption, which increases their susceptibility.
- Orthodontic Treatments: In rare cases, orthodontic treatments that put pressure on teeth, such as braces, can trigger internal root resorption.
- Inflammatory Health Conditions: Systemic inflammatory conditions, like autoimmune diseases, may indirectly impact dental health and predispose individuals to resorption.
- Unknown Causes: Sometimes, internal root resorption may occur without a clear cause, underscoring the importance of regular dental check-ups to catch issues early.
By recognizing these potential triggers, individuals can take proactive steps to minimize the risk of internal root resorption. Regular dental check-ups, prompt treatment of infections, and mindful oral care play pivotal roles in maintaining a resilient and healthy dental structure. For more information about Internal Root Resorption, please contact us.
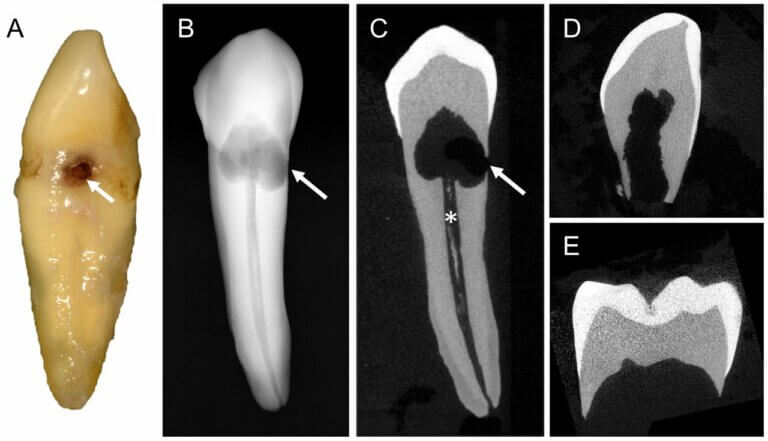
Signs And Symptoms Of Internal Root Resorption
Recognizing the symptoms of internal root resorption is crucial for timely treatment. Here’s what to look for:
- Tooth Discoloration: A pink or gray tint in the tooth is often the first noticeable sign, caused by changes in blood flow within the affected area.
- Temperature Sensitivity: Affected teeth may become sensitive to hot and cold, often due to nerve exposure as the tooth’s internal structure breaks down.
- Swelling or Pain: Inflammation within the root canal can lead to discomfort, sometimes presenting as swelling near the affected tooth.
- Dental Abscess (Pimple on the Gums): A pimple-like bump on the gumline can indicate infection, which often accompanies internal root resorption.
- Pain During Chewing: Pressure on the tooth while eating can cause pain, especially in more advanced cases.
- X-ray Evidence: Routine dental X-rays may reveal a hollow or thinning appearance in the root canal walls, a sign of resorption progression.
Being attuned to these signs allows individuals to seek prompt dental care, facilitating early diagnosis and appropriate treatment. For more information about Internal Root Resorption, please contact us.
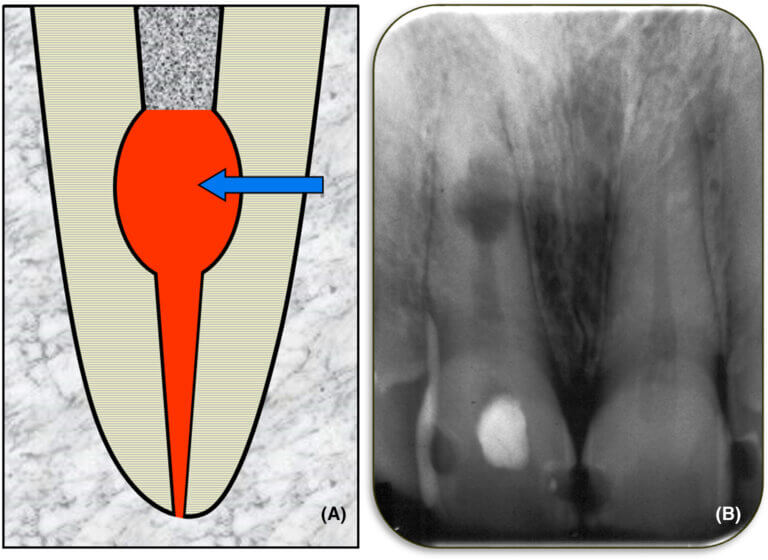
Treatment Options For Internal Root Resorption
Treating internal root resorption requires a personalized approach based on the severity of the condition. Here are the main treatment options:
- Root Canal Therapy: For early-stage resorption, root canal therapy can effectively treat the tooth by removing the affected tissue and sealing the root canal to stop the resorptive process.
- Apicoectomy (Root-End Surgery): When standard root canal therapy isn’t sufficient, apicoectomy may be considered. This involves removing the root tip and sealing the area to halt resorption.
- Tooth Extraction and Replacement: If resorption has severely compromised the tooth’s structure, extraction may be necessary. Options for tooth replacement include dental implants or bridges to restore functionality and aesthetics.
Early intervention and a proactive approach to oral health contribute significantly to the successful management of internal root resorption, preserving dental function and aesthetics. For more information about Internal Root Resorption, please contact us.
Frequently Asked Questions About Internal Root Resorption
- Is internal root resorption preventable?
While some risk factors are out of your control, such as genetic predisposition, good oral hygiene and regular dental visits can reduce your risk.
- Can internal root resorption heal on its own?
No, internal root resorption typically does not resolve on its own and requires professional treatment to prevent progression.
- What happens if internal root resorption is left untreated?
Untreated internal root resorption can lead to severe tooth pain, infection, and ultimately tooth loss.
- Can a tooth with internal root resorption still be saved?
Early detection can improve the chances of saving the tooth with treatments like root canal therapy. However, advanced cases may require extraction.
- Is internal root resorption covered by insurance?
Coverage varies by insurance plan, so check with your provider. Most dental plans cover procedures like root canals, but apicoectomies and extractions may require additional verification.
If you have more questions or think you may be experiencing symptoms of internal root resorption, don’t hesitate to contact us. At Atlas Dental, we’re here to offer expert care and guidance. Schedule a consultation to discuss any dental concerns you have.