Loose Tooth
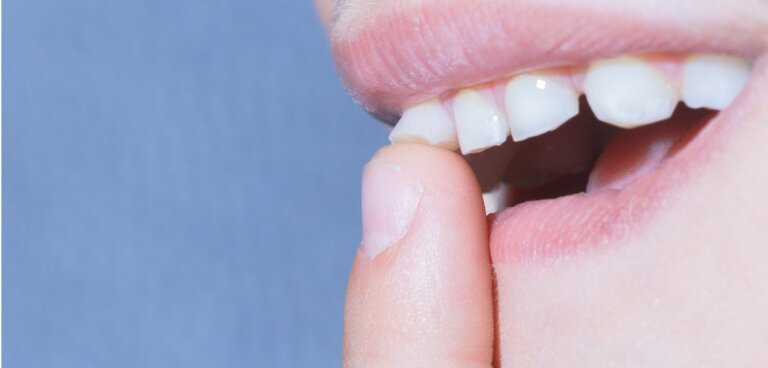
What Is A Loose Tooth?
A loose tooth occurs when a tooth loses its stability and moves within its socket. This condition can affect individuals of any age but has different implications depending on the underlying cause. In children, loose teeth signify the natural process of losing baby teeth (also known as exfoliation). However, for adults, loose teeth are often a sign of dental trauma, gum disease, or other conditions that require prompt attention.
Before you contact a Toronto dentist to examine A Loose Tooth, there are some things you should know as a patient:
- Why Do I Have A Loose Tooth?
- Signs And Symptoms Of A Loose Tooth
- Treatment Options For A Loose Tooth
- Managing A Loose Tooth Until You Can See The Dentist
- Frequently Asked Questions About Loose Teeth
If you have questions about A Loose Tooth or other dental problems, please contact us for more information.
Why Do I Have A Loose Tooth?
Several factors can contribute to a loose tooth. Understanding the cause is crucial for effective treatment.
- Dental Trauma: Injuries from accidents, sports, or falls can damage the ligaments and tissues that hold a tooth in place, leading to looseness.
- Gum Disease: Gum disease (periodontitis) is a common cause of loose teeth in adults. It weakens the gums and supporting bone, compromising tooth stability.
- Teeth Grinding (Bruxism): Chronic grinding or clenching can exert excessive pressure on teeth, causing them to loosen over time.
- Bite Misalignment: An uneven bite can create undue stress on specific teeth, leading to looseness.
- Nutritional Deficiencies or Metabolic Disorders: Conditions like scurvy (vitamin C deficiency) can weaken the gums and supporting structures of teeth.
- Natural Shedding of Baby Teeth: In children, loose teeth are a normal part of growth as adult teeth push through the gums.
It’s important to identify the cause of your loose tooth in order to receive the appropriate treatment and prevent further dental issues. If you have further questions about A Loose Tooth, please contact us.
Signs And Symptoms Of A Loose Tooth
Here are some key signs and symptoms that indicate a tooth may be loose:
- Mobility: The tooth feels wobbly when touched.
- Pain or Sensitivity: Discomfort when eating or applying pressure to the tooth.
- Swollen or Bleeding Gums: Common with gum disease or trauma.
- Visible Shifting: The tooth may appear misaligned compared to others.
- Changes in Bite: Difficulty or discomfort when chewing.
If you notice any of these symptoms, consult your dentist immediately to prevent further complications. If you have further questions about A Loose Tooth, please contact us.
Treatment Options For A Loose Tooth
The appropriate treatment depends on the cause and severity of the issue:
- Splinting: Loose teeth caused by trauma or bite issues can often be stabilized by bonding them to neighboring teeth with a dental splint.
- Deep Cleaning (Scaling and Root Planing): If gum disease is the culprit, a professional cleaning removes plaque and tartar below the gumline to encourage healing.
- Bite Adjustment: Realigning the bite can relieve uneven pressure on affected teeth.
- Extraction: Severely damaged or loose teeth may require removal, followed by replacement options like dental implants, bridges, or dentures.
- Night Guards: For bruxism, wearing a custom night guard can protect teeth from further grinding-related damage.
It’s important to discuss the benefits and risks of each treatment option with your dentist to determine the best course of action for your specific situation. In some cases, a combination of treatments may be necessary to effectively address the problem. If you have further questions about treatment options for A Loose Tooth, please contact us.
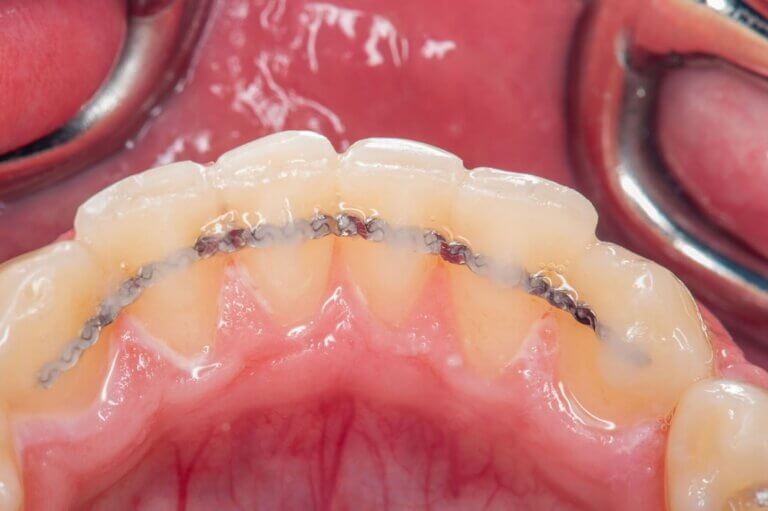
Managing A Loose Tooth Until You Can See The Dentist
If you have a loose tooth and cannot see a dentist immediately, take these steps to manage the situation:
- Avoid Hard or Sticky Foods: Stick to soft foods to prevent further stress on the tooth.
- Rinse with Salt Water: This helps reduce swelling and infection risk.
- Apply a Cold Compress: Alleviates swelling and discomfort from trauma.
- Use Orthodontic Wax: Cover sharp edges of a loose tooth to protect your gums.
- Pain Relief: Over-the-counter medications like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help manage pain temporarily.
While these steps can help manage a loose tooth in the short-term, it is important to see a dentist as soon as possible to address the underlying problem and prevent further damage or tooth loss. If you have further questions about managing A Loose Tooth, please contact us.
Frequently Asked Questions About Loose Teeth
- Is it normal for an adult to have a loose tooth?
No, a loose tooth in adults is usually a sign of an underlying dental issue, such as trauma or gum disease, and requires professional attention.
- Can a loose tooth heal on its own?
In some cases, such as mild trauma, a tooth may re-stabilize if left undisturbed. However, most loose teeth require dental treatment to prevent further damage.
- How long does it take for a loose tooth to heal after trauma?
Healing time varies, but with proper care and treatment (like splinting), a tooth may stabilize within a few weeks to months.
- What happens if I leave a loose tooth untreated?
Untreated loose teeth can lead to infection, tooth loss, or damage to surrounding teeth and gums. Prompt dental care is crucial.
A loose tooth can often be treated successfully when addressed early, making timely dental care essential. If you have further questions or concerns about loose teeth, contact our dental office for expert advice and personalized care.